Home Architects in the Enterprise: What are the IT architect types?
Based on the well-architected framework (WAF) outlined by Microsoft, developing a business solution involves focusing on five key pillars, all of them useful when talking about an IT architecture framework. These are:
While some architectural frameworks consider “Sustainability” as a sixth pillar, this discussion will concentrate on these five. Regardless of the type of architect involved, whether a Solution Architect or one specialised in a specific domain, one will apply these five pillars. Each pillar comes with its own set of recommendations, risks, and trade-offs. It’s the architect’s responsibility to strike a balance among these pillars, tailoring them to the specific requirements of the project.
WAF is mentioned here because this is fundamental for all the architects.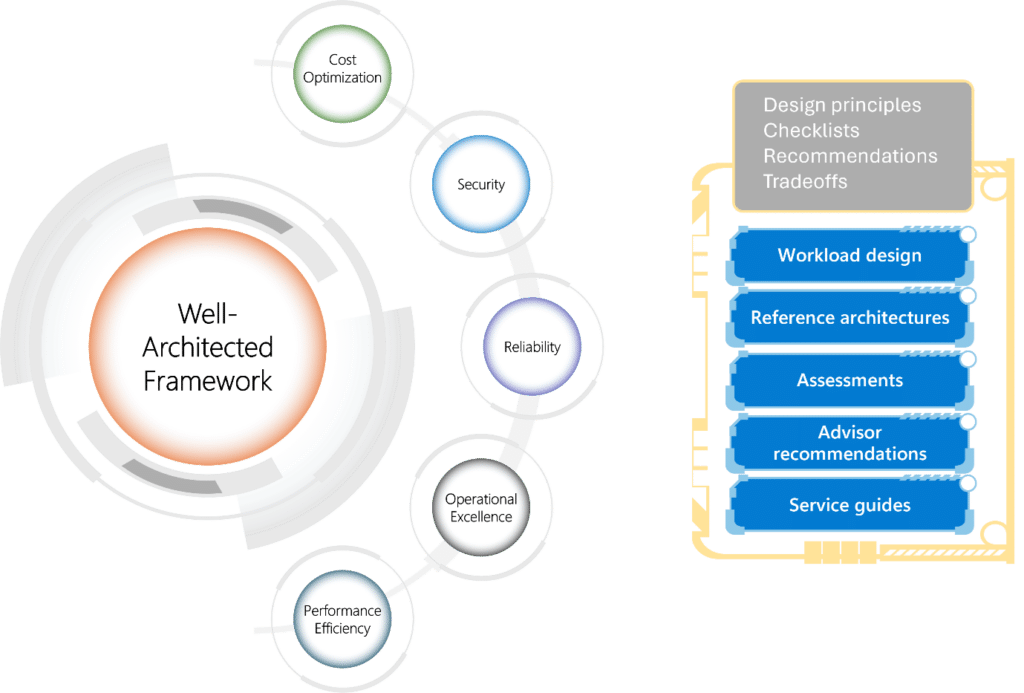
Even though WAF is simple to understand, the solution implementation methods vary from organization to organization. For instance, setting up a data platform in a startup is quite different from doing so in a large one, especially in terms of processes. While working with longstanding players, change can be challenging, and sometimes teams meant to speed up work make it more complex.
For instance, startups have one engineer to build their Data Lake while established organizations have their own enterprise architect to decide on tech to use across the organization, Solution architects to decide specific business use case in a project level and other domain specific architects to decide on how the security, network, integration, etc should work.
These unique practices in an organization’s digital architecture management pave way for creation of these specialised teams and they have their champions/architects as well.
CTO is a chief officer for all architects. He is involved in all IT decisions that effects business objectives, but he is more outwards focused rather than focused inside the organization. Followed by Enterprise architect, Solution architect, and other domain specific architects in the hierarchy. A brief explanation about individual architects in IT industry is given below, by exploring these roles, you can identify which architect position aligns best with your skills and interests, guiding you towards your future career path as a certified IT architect.
Enterprise Architects (EAs) are key in aligning an organization’s IT infrastructure with its business goals. They collaborate with the leadership team to develop technology frameworks that support immediate and future objectives. EAs ensure that IT systems are not only effective but also enhance business processes and strategic aims. This role demands IT expertise, problem-solving ability, continuous learning, and strong communication skills, enabling them to guide technology investments to be technically sound and financially viable, in line with the organization’s overarching strategic plans, they play a strong role in IT architecture governance.
Solution architects are a bridge between the problem and solution in the project level. They work closely with both business and technical team with specific business use cases. They ensure that the solution not only solves the current problem in their project but also seamlessly work for potential future use cases.
Domain Architects specialise in specific areas of enterprise architecture, focusing on particular aspects of an organization’s IT architecture strategy and implementation. They typically fall into several categories, each concentrating on a distinct domain. Common types of Domain Architects include:
Focuses on designing and optimising business processes and strategies. They align business goals with IT strategy and often work on business process management, modelling, and analysis.
Specialises in managing and designing an organization’s data infrastructure, strategy, and policies. They develop data models, design database structures, and ensure data quality and integrity.
Concentrates on the architecture of software applications within the organization. They design application structures, choose appropriate technologies, and ensure that applications align with both business needs and the overall IT infrastructure.
Also known as Infrastructure Architect, they focus on the underlying IT infrastructure, including networks, servers, storage solutions, and data centres. Their role is to design and maintain a robust, scalable, and efficient technological infrastructure.
Specialises in designing and implementing an organization’s security architecture. They develop security policies, manage risks, and ensure compliance with security standards and practices.
Plays a vital role in enabling different IT systems and components to work together efficiently. They develop a platform agnostic product that can be used by different projects to integrate their system.
Focused on cloud computing strategies, they design and manage the cloud infrastructure and services, ensuring they align with business needs and integrate effectively with existing systems.
Deals with the design and implementation of networking infrastructure, ensuring reliable, high-performance network systems that support organizational needs.
A role that can overlap with other domains, focusing on the design and implementation of specific IT systems and ensuring their alignment with business objectives.
Elastacloud
11 Toynbee Street, E1 7NE
Phone: +44 20 7859 4852
Email: info@elastacloud.com
Latest Whitepapers
Careers at Elastacloud
About Elastacloud
Learning Archives